Federal Appropriations Overview
What is Federal Appropriations?
Broadly, the Federal Appropriations process is the process through which Congress appropriates funding for federal agencies and programs. There are twelve appropriations bills that are drafted and put forward by the Appropriations Committees in the House and Senate every year. Once enacted, these bills provide specific dollar amounts and direction to the administration for agency action and programmatic funding.
The Subcommittees of the Senate Appropriations Committee
- Subcommittee on Agriculture, Rural Development, Food and Drug Administration, and Related Agencies
- Subcommittee on Commerce, Justice, Science, and Related Agencies
- Subcommittee on Defense
- Subcommittee on Energy and Water Development, and Related Agencies
- Subcommittee on Financial Services and General Government
- Subcommittee on Homeland Security
- Subcommittee on Interior, Environment, and Related Agencies
- Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Services, and Related Agencies
- Subcommittee on Legislative Branch
- Subcommittee on Military Construction, Veterans Affairs, and Related Agencies
- Subcommittee on State, Foreign Operations, and Related Programs
- Subcommittee on Transportation and Housing and Urban Development and Related Agencies
Terms to Know

Approximate Federal Appropriations Process Timeline
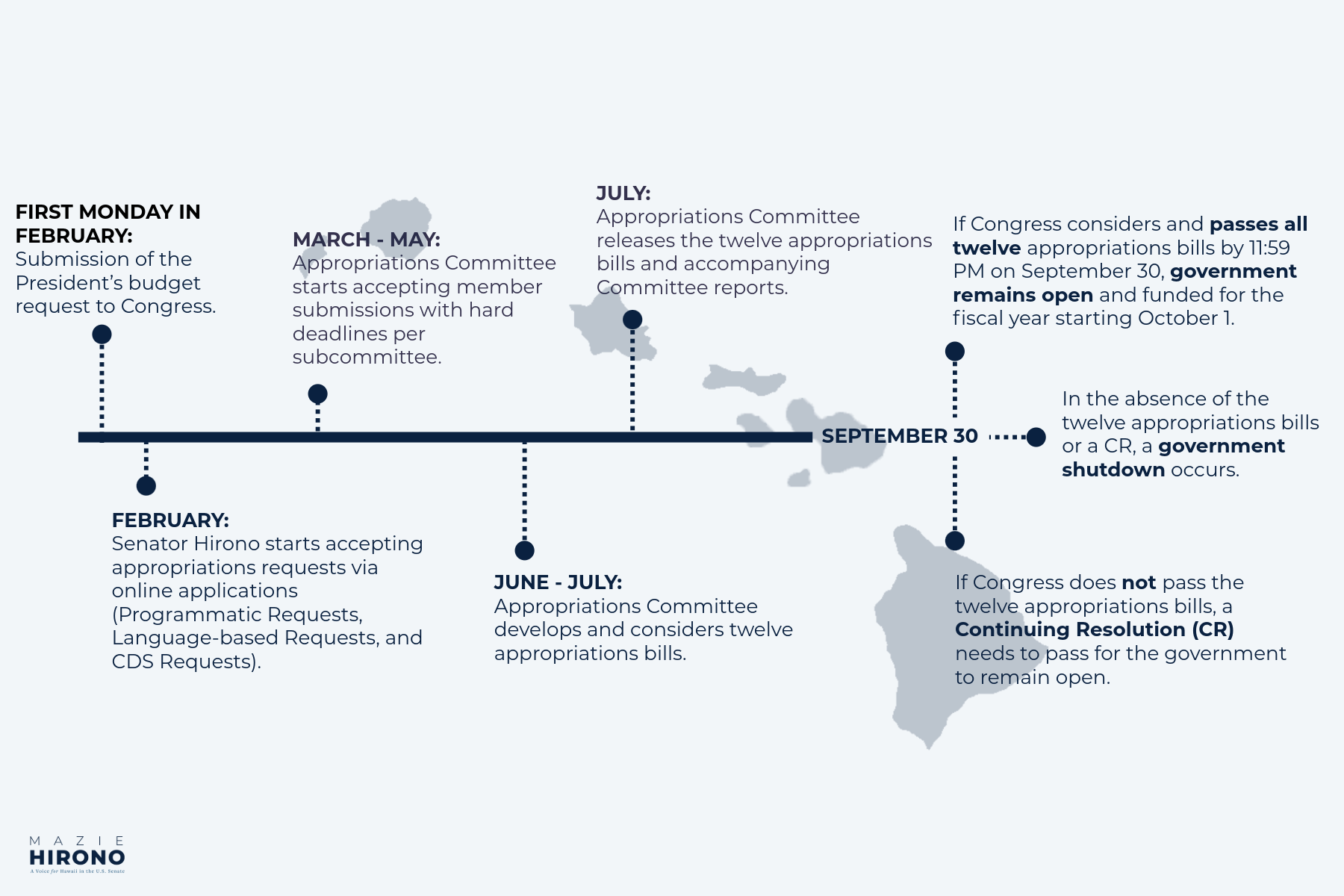
Federal Appropriations Process
Generally, the actions of the Federal Appropriations process are as follows:
-
President’s Budget Request (PBR)
- The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) submits the PBR to Congress.
- The PBR outlines the Administration’s proposed spending for the upcoming fiscal year.
-
Constituent/Stakeholder Requests
- Member offices set up a process to receive appropriations requests from constituent groups and stakeholders.
-
Types of Appropriations requests include (more details further down):
- Programmatic Requests (funding levels, bill/report language)
- Congressionally Directed Spending (CDS or “earmarks”)
- Requests are compiled by staff, approved by the Member, and submitted to the Subcommittees.
-
Appropriations Committee and Subcommittees
- Subcommittees hold preliminary hearings with agency officials to talk about the contents of the PBR.
- Subcommittees write bills and accompanying reports to be marked up and voted on and eventually sent for consideration by the full Senate.
-
Floor Consideration
- Each chamber usually considers their own versions of the twelve appropriations bills.
- There may be a debate and amendment process, depending on certain factors.
- If both chambers pass bills that are not identical, the passed bills are sent to a conference committee.
-
Conference and Final Passage:
- Differences between House and Senate versions of the bills are resolved in a conference.
- Conferenced bills must be identical and passed by both chambers, usually in a consolidated package (omnibus, minibus, cromnibus).
- Finally, the bills are sent to the President for signature or veto.
Types of Appropriations Requests
Constituents and stakeholder groups may advocate to Senators and Members of Congress for existing federal programs through Programmatic Requests. Separately, constituent and stakeholder groups may also apply for Congressionally Directed Spending (CDS or “earmarks”).
-
Programmatic Appropriations Requests seek to express support for funding a specific federal program or agency at a certain amount and/or express support for using the funding for a specific program or agency in a certain way.
- Funding Requests: Asks for a specific dollar amount for a national program (e.g., $65.115 million for the USGS National and Regional Climate Adaptation Science Centers)
- Language Requests: Asks for bill or report language that serves as directives for agencies (e.g., The committee encourages the Department to examine the prevalence and causes of behavioral health conditions among AANHPI youth, including by identifying ways the Department can address this disparity and improve access to behavioral healthcare for AANHPI youth.)
- Congressionally Directed Spending (CDS or “earmarks”) Requests seek to direct funding within a specific program or account to a specified state, local government, or nonprofit recipient and are subject to House and Senate earmark disclosure rules. This funding is meant as a one-off grant for a program or project that does not require yearly funding. Potential recipients of an earmark must be a non-profit organization or state/local government entity. All Members of Congress that submit earmark requests are required to certify that they or any members of their immediate family do not have any financial interest in any of the items requested, verified through financial certification and public disclosure of the requests on their website.